Research¶
Optical Wireless Communication¶
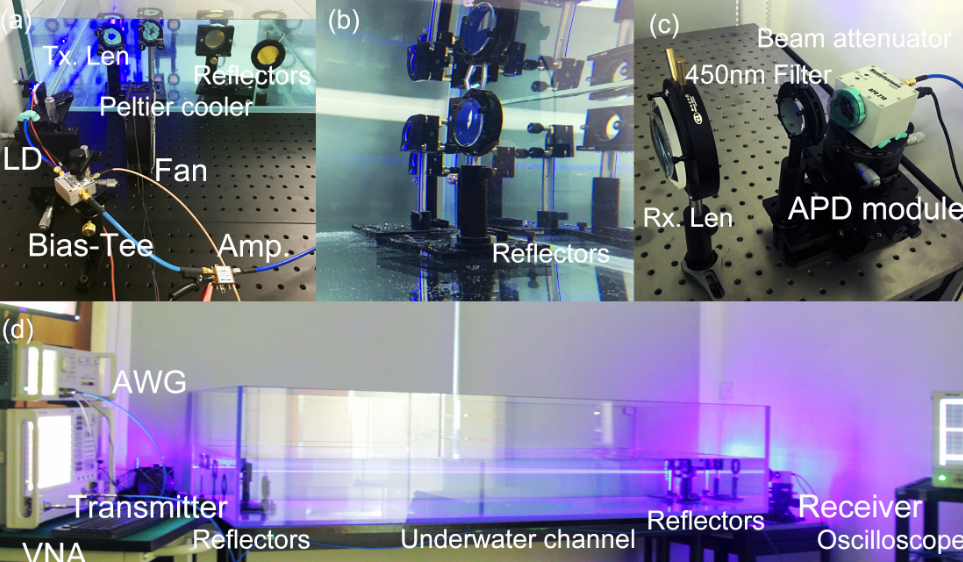
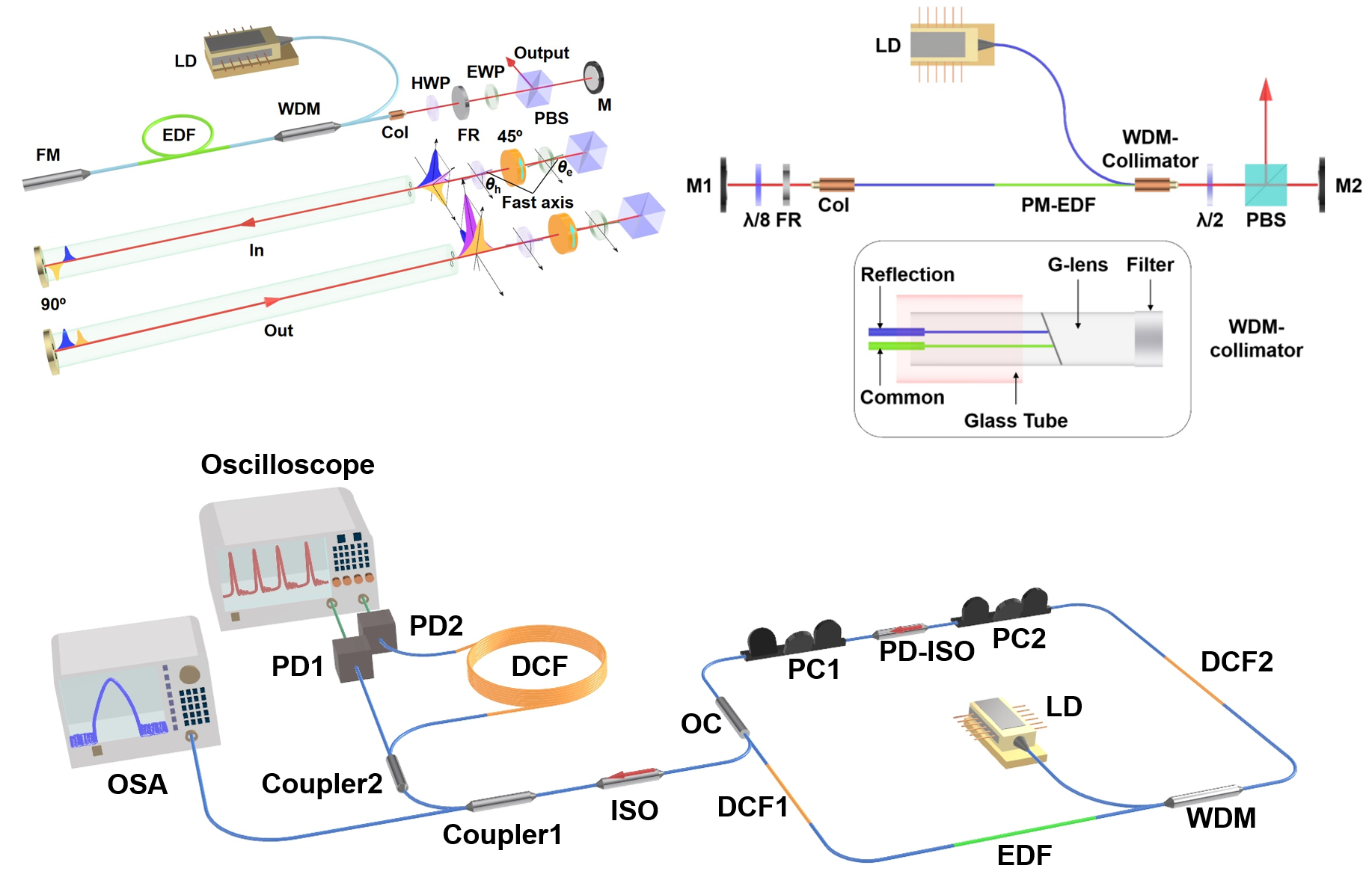
Optical Wireless Communication (OWC) is a short-range wireless access technology and an important supplement to other existing wireless communication systems. Due to the high frequency of light waves, OWC has large information carrying capacity. Light waves also have rich broadband spectrum resources and strong anti-electromagnetic interference capabilities compared with radio frequency. Recently, OWC based on high-bandwidth semiconductor light sources such as lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs) receives extensive concern. With the development of optoelectronic materials and devices, visible light communication (VLC) will not only break the capacity bottleneck up to Gbps, but also provide indoor illumination and positioning service in the future, which plays a vital role connecting the internet of things (IoT).
Silicon Photonics¶
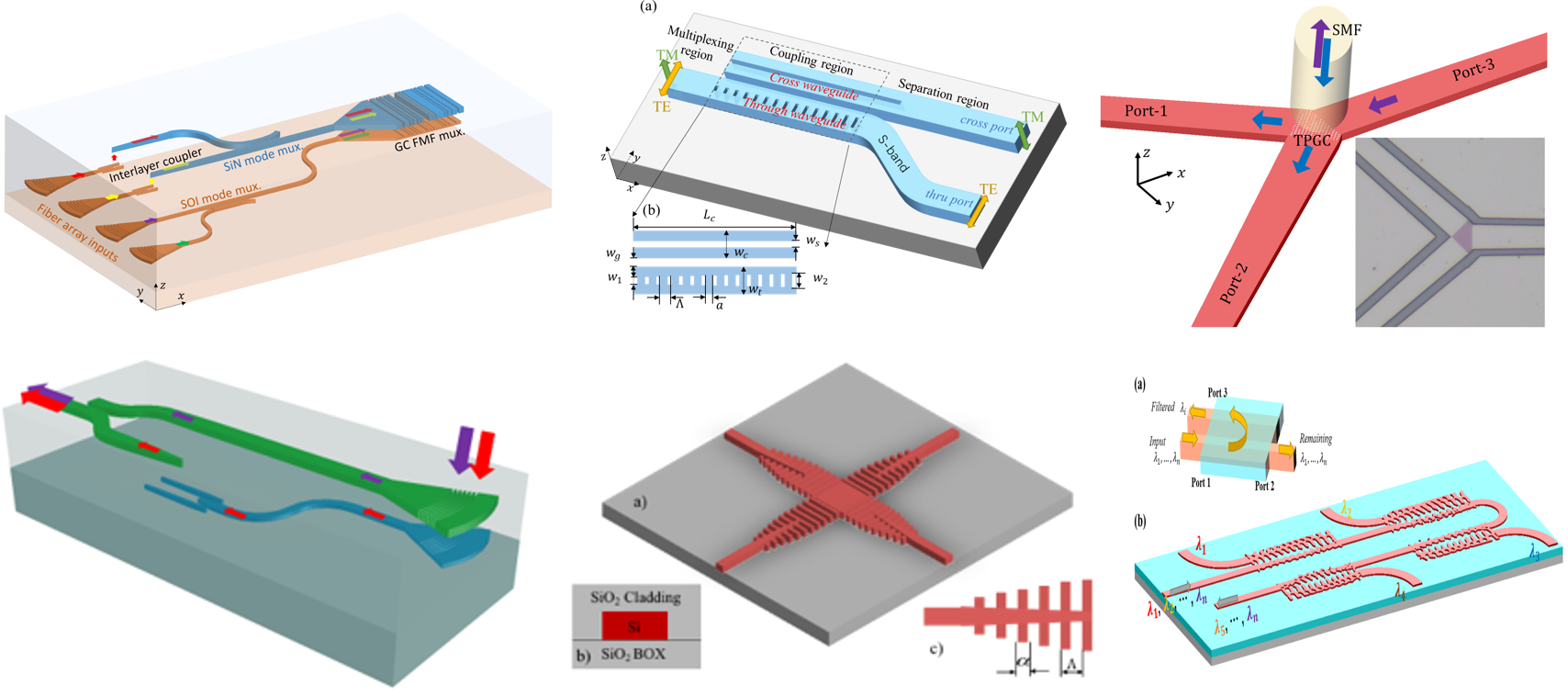
Silicon photonics is a promising solution to provide low-cost and high-performance integrated chip-based photonic devices and systems. Currently, it is commercially driven by the increasing demand for low-cost short-range optical interconnects in data centers and the computing industry. In the future, it might also be attractive for applications in biosensing and light detection and ranging (LiDAR). Our group focus on design of key passive integrated components including fiber-to-chip interface, waveguide crossings and multiplexing components (polarization, mode and wavelength division multiplexing). Apart from traditional design method based on intuition and physics, we also explore computer-automated design using advanced algorithms and deep neural networks.
Advanced Sensing Technologies¶
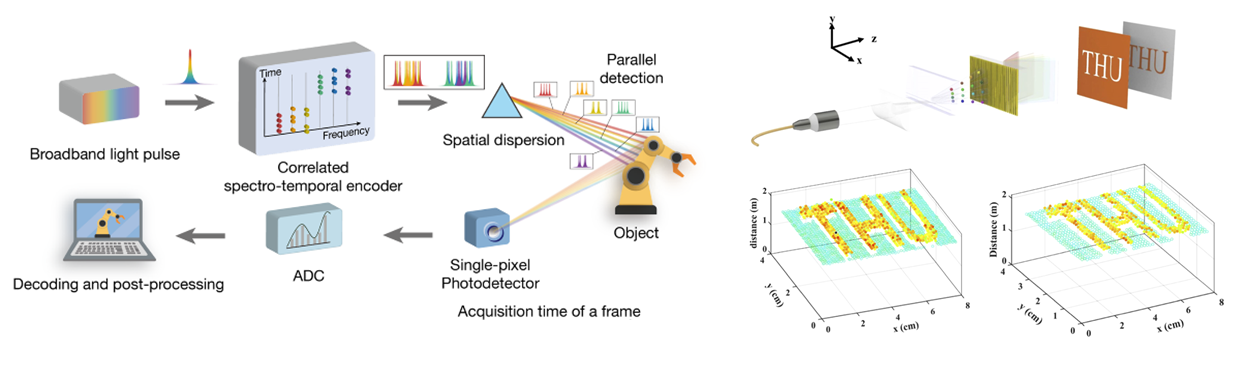
Ultrafast 3D imaging LiDAR system based on spectral scanning method: Light detection and ranging (LiDAR), as a 3D sensor, has been applied in various application scenarios, such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality (AR)/virtual reality (VR), and robots. Traditional methods based on mechanical scanning are inherently slow, bulky and prone to failure and are not well suited for the emerging applications. To adapt ultrafast imaging techniques to an ultrafast 3D imaging platform, spectrum scanning method has been proposed to be employed in LiDAR system. LiDAR group focuses on developing ultra-fast spectral scanning technology and further improving 3D imaging speed of LiDAR system.
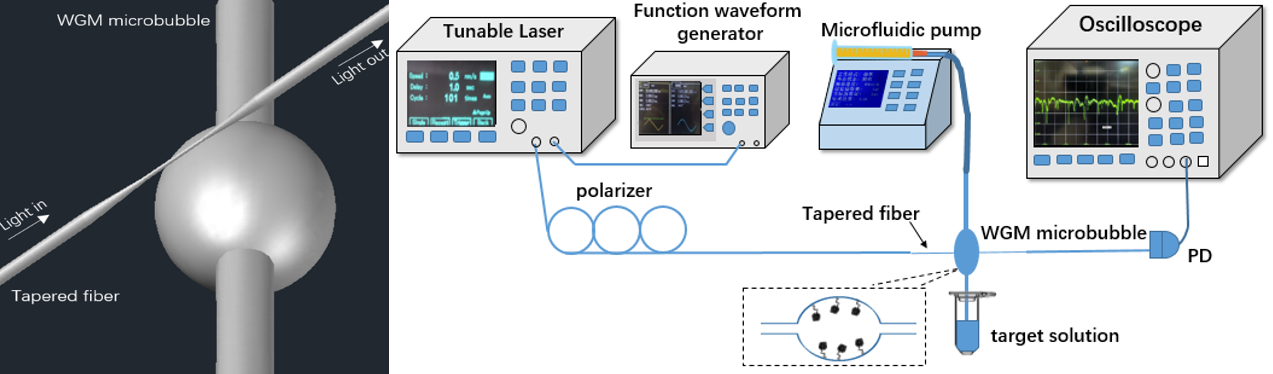
Microcavity Sensing: Whispering gallery mode (WGM) resonators, with superior performance compared with other resonators, have emerged in recent years as versatile and ultra-sensitive technology for sensing applications, which is the basis for the development of physical, chemical and biological sensors. In our research group, we use micro-cavity (e.g. Microbubble) to realize different sensing applications, such as ultra-low detection limit sensors.